How Many Miles Is Iran
 | |
| Continent | Asia |
|---|---|
| Region | Western Asia[ane] [2] [iii] |
| Coordinates | 32°00'N, 53°00'E |
| Surface area | Ranked 17th |
| • Total | 1,648,195 km2 (636,372 sq mi) |
| • Land | 99.27% |
| • Water | 0.73% |
| Coastline | two,815 km (1,749 mi) |
| Borders | Total state borders: 5,894 km (iii,662 mi) Transitional islamic state of afghanistan: 921 km (572 mi) Armenia: 44 km (27 mi) Azerbaijan (proper): 432 km (268 mi) Republic of azerbaijan (Nakhchivan exclave): 179 km (111 mi) Iraq: ane,599 km (994 mi) Pakistan: 959 km (596 mi) Turkey: 534 km (332 mi) Turkmenistan: one,148 km (713 mi) |
| Highest point | Mount Damavand 5,610 yard (18,406 ft) |
| Lowest point | Caspian Ocean −28 m (−91.9 ft) |
| Longest river | Karun |
| Largest lake | Lake Urmia |
| Exclusive economical zone | 168,718 km2 (65,142 sq mi) |
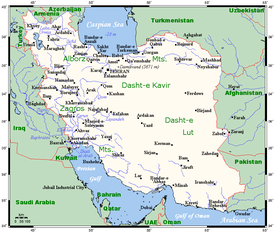
Geographically, Iran is located in Due west Asia and borders the Caspian Sea, Western farsi Gulf, and Gulf of Sultanate of oman. Its mountains have impacted both the political and the economic history of the country for several centuries. The mountains enclose several broad basins, on which major agricultural and urban settlements are located. Until the 20th century, when major highways and railroads were constructed through the mountains to connect the population centers, these basins tended to be relatively isolated from i another.

Iran map of Köppen climate classification zones

Typically, one major town dominated each bowl, and there were complex economic relationships betwixt the town and the hundreds of villages that surrounded it. In the higher elevations of the mountains rimming the basins, tribally organized groups skilful transhumance, moving with their herds of sheep and goats between traditionally established summertime and winter pastures. There are no major river systems in the country, and historically transportation was past ways of caravans that followed routes traversing gaps and passes in the mountains. The mountains likewise impeded piece of cake access to the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea.
With an area of 1,648,000 square kilometres (636,000 sq mi), Islamic republic of iran ranks seventeenth in size among the countries of the world. Iran shares its northern borders with several post-Soviet states: Armenia, Republic of azerbaijan,[a] and Turkmenistan. These borders extend for more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi), including nearly 650 kilometres (400 mi) of water along the southern shore of the Caspian Body of water. Islamic republic of iran'southward western borders are with Turkey in the north and Iraq in the south, terminating at the Arvand Rud.
The Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman littorals grade the entire i,770 kilometres (i,100 mi) southern border. To the e lie Transitional islamic state of afghanistan on the n and Pakistan on the far s. Iran'south diagonal distance from Republic of azerbaijan in the northwest to Sistan and Baluchestan Province in the southeast is approximately 2,333 kilometres (ane,450 mi).
Topography [edit]


The topography of Islamic republic of iran consists of rugged, mountainous rims surrounding high interior basins. The main mountain concatenation is the Zagros Mountains, a serial of parallel ridges interspersed with plains that bisect the country from northwest to southeast. Many peaks in the Zagros exceed 3,000 metres (ix,843 ft) above ocean level, and in the south-central region of the country in that location are at least v peaks that are over 4,000 metres (13,123 ft).
As the Zagros continue into southeastern Iran, the average elevation of the peaks declines dramatically to under one,500 metres (iv,921 ft). Rimming the Caspian Sea littoral is another chain of mountains, the narrow just high Alborz Mountains. Volcanic Mount Damavand, 5,610 metres (18,406 ft), located in the center of the Alborz, is not only the state'south highest elevation simply also the highest mount on the Eurasian landmass west of the Hindu Kush.
The center of Iran consists of several closed basins that collectively are referred to as the Central Plateau. The boilerplate elevation of this plateau is nigh 900 metres (2,953 ft), only several of the mountains that tower over the plateau exceed 3,000 metres (9,843 ft). The eastern role of the plateau is covered by two salt deserts, the Dasht-e Kavir (Swell Common salt Desert) and the Dasht-eastward Lut. Except for some scattered oases, these deserts are uninhabited.
Parts of northwestern Iran are office of the Armenian highlands, which adjoins it topographically with other parts of neighbouring Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia.[4]
Iran has only two expanses of lowlands: the Khuzestan Plain in the southwest and the Caspian Sea coastal plain in the n. The onetime is a roughly triangular-shaped extension of the Mesopotamia plainly and averages almost 160 kilometres (99 mi) in width. It extends for about 120 kilometres (75 mi) inland, barely rising a few meters above sea level, so meets abruptly with the get-go foothills of the Zagros. Much of the Khuzestan plain is covered with marshes.
The Caspian patently is both longer and narrower. It extends for some 640 kilometres (400 mi) along the Caspian shore, but its widest point is less than 50 kilometres (31 mi), while at some places less than ii kilometres (1.ii mi) separate the shore from the Alborz foothills. The Western farsi Gulf declension southward of Khuzestan and the Gulf of Sultanate of oman declension have no real plains because the Zagros in these areas come right down to the shore.
There are no major rivers in the country. Of the small rivers and streams, the only ane that is navigable is the 830 kilometres (520 mi)-long Karun, which shallow-draft boats can negotiate from Khorramshahr to Ahvaz, a distance of about 180 kilometres (110 mi). Other major rivers include the Karkheh, spanning 700 kilometres (430 mi) and joining the Tigris; and the Zayandeh River, which is 300 kilometres (190 mi) long. Several other permanent rivers and streams as well bleed into the Persian Gulf, while a number of small-scale rivers that originate in the northwestern Zagros or Alborz bleed into the Caspian Sea.
On the Cardinal Plateau, numerous rivers—almost of which have dry beds for the greater role of the year—form from snow melting in the mountains during the spring and flow through permanent channels, draining eventually into salt lakes that also tend to dry upwardly during the summertime months. In that location is a permanent salt lake, Lake Urmia (the traditional name, also cited as Lake Urmiyeh, to which it has reverted later on being called Lake Rezaiyeh under Mohammad Reza Shah), in the northwest, whose brine content is as well high to back up fish or most other forms of aquatic life. In that location are also several connected salt lakes along the Iran-Transitional islamic state of afghanistan border in the province of Baluchestan va Sistan.
Islamic republic of iran's highlands are home to some of the earth's nearly unexpected glaciers. Their appearance in the dry environment is advantageous for those who depend on glacial ice as a supply of fresh water. In an trek, Klaus Thymann together with the environmental charity Project Pressure level produced a series of annal and expedition photographs that depict the urgency of the situation surrounding climate change and the individuals who rely on such natural water ice forms to sustain life in remote areas.[v]

Mount Damavand. Photograph by Klaus Thymann, 2014.
A recent global remote sensing assay suggested that there were 1,481 km² of tidal flats in Islamic republic of iran, making information technology the 22nd ranked country in terms of tidal flat area.[6]
Climate [edit]
Iran has a variable climate. In the northwest, winters are cold with heavy snowfall and subfreezing temperatures. Spring and fall are relatively mild, while summers are dry and hot. In the south, winters are mild and the summers are very hot, having average daily temperatures in July exceeding 38 °C (100.4 °F). On the Khuzestan Plainly, summer rut is accompanied by high humidity.
In full general, Iran has a continental climate in which almost of the relatively scant annual atmospheric precipitation falls from Oct through April. In most of the country, yearly precipitation averages 400 millimetres (15.7 in) or less. The major exceptions are the higher mountain valleys of the Zagros and the Caspian littoral evidently, where precipitation averages at least 600 millimetres (24 in) and is in the form of snow at high altitudes. In the western function of the Caspian, rainfall exceeds ane,500 millimetres (59 in) annually and is distributed relatively evenly throughout the yr. This contrasts with some basins of the Central Plateau that receive 100 millimetres (iv in) or less of precipitation. Iran is considered colder than neighboring countries such as Iraq and Turkmenistan, due to its higher tiptop.
| | Caspian mild and wet Caspian mild Mediterranean with leap rains Mediterranean Cold mountains Very cold mountains Common cold semi-desert Hot semi-desert Dry desert Hot dry desert Hot coastal dry out Coastal dry |
Examples [edit]
| Climate data for Tehran Mehrabad - Altitude: 1190.8 thousand (1951-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record loftier °C (°F) | 19.vi (67.3) | 23.0 (73.4) | 29.4 (84.9) | 33.4 (92.1) | 37.0 (98.6) | 41.0 (105.8) | 43.0 (109.4) | 42.0 (107.6) | 38.0 (100.4) | 33.four (92.ane) | 26.four (79.5) | 21.0 (69.8) | 43.0 (109.four) |
| Average high °C (°F) | vii.ix (46.ii) | x.6 (51.1) | 15.7 (sixty.iii) | 22.2 (72.0) | 28.0 (82.4) | 34.0 (93.2) | 36.7 (98.1) | 35.7 (96.3) | 31.six (88.9) | 24.5 (76.1) | sixteen.three (61.iii) | 10.ane (50.2) | 22.viii (73.0) |
| Daily hateful °C (°F) | 3.8 (38.eight) | half dozen.0 (42.8) | 10.7 (51.3) | xvi.eight (62.2) | 22.1 (71.eight) | 27.5 (81.v) | 30.iii (86.5) | 29.v (85.1) | 25.5 (77.9) | 19.0 (66.2) | 11.half dozen (52.9) | 5.nine (42.half-dozen) | 17.4 (63.3) |
| Boilerplate low °C (°F) | −0.4 (31.3) | i.four (34.5) | 5.7 (42.iii) | 11.4 (52.5) | 16.three (61.iii) | 21.1 (lxx.0) | 24.0 (75.ii) | 23.4 (74.1) | xix.iv (66.nine) | xiii.5 (56.3) | half dozen.8 (44.2) | 1.8 (35.2) | 12.0 (53.7) |
| Record depression °C (°F) | −15.0 (5.0) | −xiii.0 (eight.half dozen) | −8.0 (17.half-dozen) | −4.0 (24.eight) | 2.4 (36.three) | five.0 (41.0) | 14.0 (57.two) | 13.0 (55.4) | ix.0 (48.ii) | two.8 (37.0) | −7.0 (xix.4) | −xiii.0 (8.half dozen) | −15.0 (5.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 34.half-dozen (1.36) | 33.two (1.31) | 39.6 (1.56) | 31.9 (ane.26) | xiv.viii (0.58) | 3.0 (0.12) | 2.two (0.09) | 1.seven (0.07) | 1.ii (0.05) | x.7 (0.42) | 26.1 (1.03) | 33.7 (1.33) | 232.7 (9.18) |
| Average precipitation days | 9.0 | 8.half dozen | 10.7 | x.8 | 8.viii | iii.1 | 2.one | one.3 | i.one | 5.3 | vii.2 | 8.six | 76.half-dozen |
| Average snowy days | 5.one | 2.9 | i.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 12.3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 64 | 56 | 47 | 40 | 33 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 27 | 36 | 49 | 62 | 41 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 168.8 | 179.viii | 203.0 | 220.6 | 287.0 | 346.3 | 345.nine | 333.6 | 302.8 | 249.nine | 202.9 | 168.9 | 3,009.5 |
| Boilerplate ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | iii | five | half dozen | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Source 1: Iran Meteorological Organization (records),[seven] (temperatures),[8] (precipitation),[9] (humidity),[10] (days with precipitation),[11] [12] (sunshine)[xiii] | |||||||||||||
| Source two: Weather Atlas (UV),[xiv] | |||||||||||||
| Climate information for Tehran-Shomal (northward of Tehran), altitude: 1549.1 one thousand, from 1988–2010. | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Tape high °C (°F) | 17.ii (63.0) | 21.2 (lxx.2) | 29.0 (84.2) | 32.iv (90.3) | 33.6 (92.5) | 39.ii (102.6) | 40.4 (104.7) | 39.6 (103.iii) | 36.2 (97.2) | 31.2 (88.2) | 23.half dozen (74.5) | 19.half dozen (67.3) | 40.4 (104.vii) |
| Average high °C (°F) | vi.1 (43.0) | 8.half dozen (47.five) | 13.8 (56.eight) | 20.0 (68.0) | 25.5 (77.9) | 31.half-dozen (88.9) | 34.4 (93.9) | 33.half-dozen (92.5) | 29.five (85.1) | 22.eight (73.0) | 14.5 (58.1) | 8.6 (47.v) | 20.8 (69.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.3 (36.i) | 4.4 (39.9) | 9.two (48.six) | xiv.9 (58.8) | 19.8 (67.6) | 25.6 (78.1) | 28.5 (83.3) | 27.half-dozen (81.7) | 23.4 (74.ane) | 17.2 (63.0) | 9.9 (49.viii) | 4.viii (40.6) | 15.6 (sixty.one) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.5 (29.3) | 0.2 (32.iv) | four.6 (40.iii) | 9.8 (49.6) | 14.ii (57.vi) | nineteen.7 (67.five) | 22.vi (72.7) | 21.vi (70.ix) | 17.3 (63.i) | 11.vii (53.1) | 5.iii (41.five) | 0.9 (33.6) | 10.five (51.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −thirteen.0 (8.6) | −eleven.0 (12.ii) | −8.0 (17.6) | −1.6 (29.i) | 3.0 (37.4) | 12.0 (53.six) | 15.4 (59.7) | 13.5 (56.3) | 8.eight (47.viii) | ii.6 (36.seven) | −v.2 (22.vi) | −nine.6 (xiv.seven) | −13.0 (8.6) |
| Boilerplate atmospheric precipitation mm (inches) | 61.9 (2.44) | 68.3 (2.69) | 73.9 (2.91) | 53.2 (two.09) | 24.0 (0.94) | four.9 (0.19) | 3.viii (0.15) | 2.5 (0.ten) | 3.viii (0.fifteen) | 18.4 (0.72) | 41.5 (i.63) | 64.3 (2.53) | 420.five (16.54) |
| Average precipitation days | 12.iii | 10.9 | 12.3 | 10.0 | 8.9 | three.iii | 3.iv | 1.half dozen | 1.iii | five.eight | eight.6 | 10.7 | 89.i |
| Boilerplate snowy days | 8.nine | 6.6 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 0.i | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | four.9 | 23.vii |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 67 | 59 | 53 | 44 | 39 | 30 | 31 | 31 | 33 | 44 | 57 | 66 | 46 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 135.eight | 146.four | 185.ane | 215.0 | 274.vi | 322.8 | 331.8 | 327.v | 292.half dozen | 245.5 | 171.five | 135.8 | 2,784.iv |
| Source: [15] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Mashhad (1951–2010, extremes 1951–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calendar month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | October | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record loftier °C (°F) | twenty.0 (68.0) | 22.0 (71.6) | 28.0 (82.4) | 30.4 (86.7) | 35.2 (95.4) | 38.six (101.5) | 43.8 (110.8) | 40.4 (104.seven) | 38.0 (100.4) | 33.8 (92.8) | 28.iv (83.1) | 22.2 (72.0) | 43.eight (110.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | half dozen.one (43.0) | 7.iii (45.1) | 12.2 (54.0) | 17.9 (64.2) | 24.eight (76.6) | thirty.3 (86.5) | 32.iv (xc.3) | 31.1 (88.0) | 25.9 (78.six) | 20.five (68.nine) | 13.5 (56.iii) | eight.1 (46.6) | 21.2 (lxx.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.7 (35.1) | 3.7 (38.7) | 8.5 (47.3) | xiv.7 (58.5) | 19.vi (67.3) | 24.four (75.9) | 26.six (79.nine) | 24.8 (76.vi) | 20.iii (68.5) | 14.5 (58.i) | 8.vii (47.7) | iv.0 (39.2) | xiv.3 (57.vii) |
| Boilerplate low °C (°F) | −5.8 (21.6) | −4.3 (24.3) | 2.9 (37.2) | half dozen.4 (43.5) | 10.4 (50.7) | 14.4 (57.ix) | xvi.seven (62.1) | xiv.5 (58.1) | nine.seven (49.five) | iv.four (39.nine) | −1.9 (28.vi) | −iii.7 (25.iii) | 7.3 (45.ane) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −27.0 (−16.half dozen) | −32.0 (−25.6) | −13.0 (8.6) | −7.0 (19.4) | −1.0 (30.2) | 4.0 (39.2) | 10.0 (l.0) | five.0 (41.0) | −1.0 (30.2) | −8.0 (17.half-dozen) | −xvi.0 (3.2) | −25.0 (−13.0) | −32.0 (−25.6) |
| Boilerplate precipitation mm (inches) | 32.6 (i.28) | 34.five (1.36) | 55.v (2.nineteen) | 45.4 (ane.79) | 27.2 (1.07) | four.0 (0.sixteen) | 1.1 (0.04) | 0.vii (0.03) | 2.1 (0.08) | 8.0 (0.31) | 16.one (0.63) | 24.3 (0.96) | 251.v (9.90) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 5.half dozen | 5.eight | 8.2 | 6.8 | iv.five | 1.i | 0.iii | 0.2 | 0.5 | ane.5 | 2.9 | 4.ii | 41.6 |
| Average snowy days | 5.6 | 5.8 | 4.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.i | 1.2 | 3.viii | 20.9 |
| Boilerplate relative humidity (%) | 75 | 73 | 69 | 62 | 50 | 37 | 34 | 33 | 37 | 49 | 63 | 73 | 54 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 148.3 | 147.five | 163.3 | 200.four | 280.4 | 343.2 | 366.ix | 359.7 | 305.two | 249.5 | 188.three | 151.six | 2,904.3 |
| Source: Iran Meteorological Arrangement (records),[16] (temperatures),[17] (atmospheric precipitation),[18] (humidity),[19] (days with precipitation),[20] [21] (sunshine)[22] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Isfahan (1961–1990, extremes 1951–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | October | Nov | December | Year |
| Tape high °C (°F) | xx.4 (68.7) | 23.4 (74.one) | 29.0 (84.2) | 32.0 (89.half-dozen) | 37.6 (99.7) | 41.0 (105.8) | 43.0 (109.iv) | 42.0 (107.6) | 39.0 (102.2) | 33.ii (91.viii) | 26.8 (80.2) | 21.2 (seventy.2) | 43.0 (109.four) |
| Boilerplate high °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) | xi.9 (53.4) | xvi.viii (62.2) | 22.0 (71.6) | 28.0 (82.iv) | 34.1 (93.four) | 36.four (97.5) | 35.1 (95.2) | 31.2 (88.two) | 24.4 (75.9) | sixteen.9 (62.4) | ten.8 (51.four) | 23.0 (73.four) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.nine) | 5.5 (41.9) | 10.4 (50.seven) | 15.7 (lx.3) | 21.3 (seventy.three) | 27.1 (80.8) | 29.four (84.9) | 27.9 (82.2) | 23.5 (74.3) | xvi.ix (62.iv) | nine.9 (49.8) | 4.4 (39.9) | 16.ii (61.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.4 (27.7) | −0.2 (31.vi) | 4.5 (40.1) | nine.4 (48.9) | 14.2 (57.6) | 19.ane (66.four) | 21.5 (70.7) | nineteen.eight (67.6) | fifteen.ane (59.ii) | nine.3 (48.7) | 3.6 (38.5) | −0.nine (thirty.4) | 9.iv (48.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −19.4 (−2.nine) | −12.2 (10.0) | −eight.0 (17.6) | −4.0 (24.eight) | 4.v (xl.ane) | ten.0 (50.0) | thirteen.0 (55.4) | 11.0 (51.eight) | 5.0 (41.0) | 0.0 (32.0) | −eight.0 (17.6) | −13.0 (8.6) | −nineteen.4 (−two.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 17.ane (0.67) | 14.ane (0.56) | 18.2 (0.72) | nineteen.2 (0.76) | 8.viii (0.35) | 0.6 (0.02) | 0.7 (0.03) | 0.2 (0.01) | 0.0 (0.0) | 4.1 (0.sixteen) | 9.9 (0.39) | xix.6 (0.77) | 112.5 (4.43) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ ane.0 mm) | 4.0 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 3.five | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.one | 0.0 | 0.eight | ii.2 | iii.7 | 23.5 |
| Average snowy days | 3.2 | 1.7 | 0.seven | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 1.nine | 7.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | lx | 51 | 43 | 39 | 33 | 23 | 23 | 24 | 26 | 36 | 48 | 57 | 39 |
| Hateful monthly sunshine hours | 205.three | 213.3 | 242.one | 244.five | 301.3 | 345.4 | 347.six | 331.2 | 311.6 | 276.v | 226.1 | 207.6 | iii,252.5 |
| Source 1: NOAA[23] | |||||||||||||
| Source ii: Iran Meteorological Organisation (records)[24] [25] | |||||||||||||
| Climate information for Karaj (1985–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | January | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | xviii.2 (64.8) | 19.viii (67.vi) | 27.4 (81.3) | 33.0 (91.4) | 34.6 (94.3) | 39.2 (102.6) | 42.0 (107.half-dozen) | xl.2 (104.4) | 37.2 (99.0) | 31.viii (89.2) | 25.0 (77.0) | 20.0 (68.0) | 42.0 (107.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | half dozen.1 (43.0) | 9.0 (48.2) | fourteen.2 (57.6) | 20.7 (69.3) | 26.2 (79.two) | 32.6 (ninety.7) | 35.ii (95.4) | 34.5 (94.i) | xxx.4 (86.7) | 23.5 (74.three) | 15.i (59.2) | eight.9 (48.0) | 21.4 (seventy.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | one.8 (35.2) | 4.one (39.4) | 8.seven (47.7) | 14.5 (58.1) | 19.2 (66.6) | 24.6 (76.3) | 27.1 (fourscore.viii) | 26.8 (80.2) | 22.9 (73.two) | 17.i (62.8) | 9.nine (49.8) | 4.6 (40.3) | fifteen.one (59.2) |
| Boilerplate low °C (°F) | −2.5 (27.5) | −0.7 (xxx.7) | iii.2 (37.viii) | 8.4 (47.1) | 12.two (54.0) | 16.v (61.seven) | 19.0 (66.ii) | nineteen.1 (66.4) | fifteen.3 (59.five) | 10.8 (51.4) | iv.8 (xl.6) | 0.3 (32.5) | 8.9 (48.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −19.0 (−2.2) | −15.6 (3.9) | −10.5 (13.ane) | −3.v (25.7) | −0.iv (31.3) | vii.two (45.0) | x.half-dozen (51.one) | 12.0 (53.6) | vii.0 (44.vi) | −0.five (31.1) | −half-dozen.0 (21.2) | −14.vi (5.7) | −19.0 (−ii.2) |
| Average atmospheric precipitation mm (inches) | xxx.eight (one.21) | 32.i (1.26) | 45.4 (i.79) | 39.1 (i.54) | 19.5 (0.77) | 2.seven (0.11) | 3.0 (0.12) | 1.two (0.05) | 1.half-dozen (0.06) | 15.ane (0.59) | 27.7 (one.09) | 33.5 (1.32) | 251.vii (9.91) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | vi.3 | 5.7 | 6.vii | 5.8 | 3.7 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.iii | 3.2 | iv.8 | 5.8 | 44.3 |
| Average snowy days | five.4 | 3.7 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.five | 2.7 | 14.3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 67 | 60 | 53 | 48 | 43 | 34 | 35 | 34 | 36 | 44 | 56 | 66 | 48 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 166.three | 169.7 | 197.4 | 218.i | 280.7 | 335.2 | 341.five | 340.one | 304.2 | 250.one | 187.2 | 156.8 | 2,947.3 |
| Source: Iran Meteorological Organization (records),[26] (temperatures),[8] (precipitation),[9] (humidity),[10] (days with precipitation and snow),[27] (sunshine)[28] | |||||||||||||
| Climate information for Shiraz (1961–1990, extremes 1951–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | November | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.4 (72.3) | 24.0 (75.two) | 30.half dozen (87.1) | 34.0 (93.two) | 38.6 (101.5) | 42.0 (107.6) | 43.ii (109.8) | 42.0 (107.6) | 39.0 (102.2) | 34.4 (93.nine) | 28.4 (83.ane) | 23.2 (73.8) | 43.two (109.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.1 (53.8) | fourteen.7 (58.v) | 18.9 (66.0) | 23.8 (74.8) | xxx.vi (87.i) | 36.1 (97.0) | 37.8 (100.0) | 37.0 (98.half dozen) | 33.7 (92.7) | 27.8 (82.0) | 20.v (68.nine) | 14.iv (57.ix) | 25.6 (78.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | five.3 (41.v) | 7.7 (45.nine) | eleven.eight (53.two) | 16.2 (61.two) | 22.five (72.5) | 27.7 (81.9) | 29.8 (85.six) | 28.7 (83.7) | 24.5 (76.1) | 18.four (65.one) | xi.7 (53.one) | half dozen.8 (44.2) | 17.6 (63.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.four (31.iii) | 1.2 (34.two) | iv.8 (40.vi) | viii.5 (47.3) | thirteen.2 (55.8) | 17.1 (62.8) | nineteen.ix (67.viii) | 18.8 (65.8) | fourteen.1 (57.four) | viii.8 (47.8) | 3.8 (38.8) | 0.v (32.nine) | 9.2 (48.6) |
| Record depression °C (°F) | −14.0 (6.viii) | −8.0 (17.6) | −4.0 (24.eight) | −two.0 (28.4) | three.0 (37.4) | 9.0 (48.2) | 14.0 (57.2) | 12.0 (53.six) | one.0 (33.8) | one.six (34.nine) | −eight.0 (17.half dozen) | −11.0 (12.2) | −14.0 (half-dozen.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 79.8 (3.xiv) | 49.eight (1.96) | 48.four (i.91) | 30.6 (one.20) | vi.six (0.26) | 0.2 (0.01) | one.0 (0.04) | 0.1 (0.00) | 0.0 (0.0) | five.2 (0.xx) | 20.vii (0.81) | 63.two (2.49) | 305.6 (12.03) |
| Boilerplate rainy days | 8.vii | vii.9 | 7.ix | half-dozen.4 | 2.ane | 0.2 | 0.viii | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.two | iii.7 | 7.2 | 46.6 |
| Average snowy days | i.v | 0.vi | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.half-dozen | two.vii |
| Boilerplate relative humidity (%) | 65 | 58 | 51 | 46 | 32 | 22 | 24 | 24 | 26 | 34 | 48 | 61 | 41 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 217.0 | 218.5 | 236.two | 247.seven | 324.one | 357.eight | 344.6 | 329.7 | 318.0 | 297.7 | 238.iii | 216.2 | 3,345.viii |
| Source 1: NOAA[29] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Iran Meteorological Organization (records)[30] [31] | |||||||||||||
| Climate information for Tabriz (1951–2010, extremes 1951–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calendar month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record loftier °C (°F) | xvi.0 (60.eight) | 19.0 (66.ii) | 25.6 (78.1) | 31.ii (88.2) | 33.8 (92.8) | 39.0 (102.2) | 42.0 (107.6) | 41.0 (105.8) | 38.0 (100.4) | 30.6 (87.1) | 23.4 (74.1) | 21.8 (71.2) | 42.0 (107.six) |
| Boilerplate high °C (°F) | 2.3 (36.i) | 4.ix (40.8) | 10.six (51.ane) | 17.0 (62.6) | 22.8 (73.0) | 28.8 (83.8) | 32.8 (91.0) | 32.seven (90.ix) | 28.iii (82.9) | 20.7 (69.3) | 12.0 (53.6) | 5.two (41.4) | eighteen.2 (64.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) | 0.5 (32.9) | five.6 (42.one) | eleven.v (52.7) | 16.7 (62.1) | 22.1 (71.viii) | 26.0 (78.eight) | 25.9 (78.six) | 21.four (seventy.5) | 14.5 (58.1) | seven.i (44.8) | ane.2 (34.ii) | 12.6 (54.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −v.seven (21.7) | −3.9 (25.0) | 0.vi (33.1) | 6.0 (42.8) | 10.vii (51.3) | 15.4 (59.7) | 19.3 (66.7) | 19.1 (66.4) | xiv.5 (58.ane) | 8.4 (47.one) | 2.one (35.8) | −2.9 (26.viii) | 7.0 (44.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −30.0 (−22.0) | −25.0 (−thirteen.0) | −20.0 (−4.0) | −fifteen.0 (5.0) | 0.6 (33.ane) | 4.0 (39.two) | 7.0 (44.vi) | 10.0 (50.0) | four.0 (39.ii) | −4.0 (24.8) | −17.0 (1.iv) | −23.5 (−x.iii) | −30.0 (−22.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 24.0 (0.94) | 28.2 (ane.11) | 45.0 (1.77) | 56.6 (2.23) | 43.1 (one.70) | 19.four (0.76) | five.half dozen (0.22) | three.3 (0.13) | 10.9 (0.43) | 24.5 (0.96) | 30.one (1.19) | 24.1 (0.95) | 318.8 (12.55) |
| Average rainy days | half dozen.nine | 7.3 | 10.7 | 14.8 | 9.iii | 3.2 | one.2 | 0.vi | 1.9 | iv.9 | 5.v | half dozen.3 | 72.half dozen |
| Average snowy days | eleven.3 | nine.nine | v.9 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 1.8 | 8.2 | 38.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 72 | 69 | 61 | 56 | 50 | 40 | 36 | 36 | 39 | 51 | 65 | 71 | 53 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 125.9 | 146.3 | 179.7 | 200.8 | 268.7 | 334.3 | 352.v | 337.vii | 301.4 | 231.6 | 180.iii | 136.8 | 2,796 |
| Source: Iran Meteorological Organization (records),[32] (temperatures),[33] (precipitation),[34] (humidity),[35] (days with precipitation),[36] [37] (sunshine)[38] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Qom (1986–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | April | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | November | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 23.iv (74.ane) | 26.5 (79.7) | 35.5 (95.9) | 36.5 (97.vii) | 41.5 (106.7) | 44.two (111.half-dozen) | 47.0 (116.6) | 45.5 (113.ix) | 41.6 (106.9) | 36.half dozen (97.9) | 28.6 (83.5) | 22.5 (72.five) | 47.0 (116.vi) |
| Average high °C (°F) | ten.2 (50.4) | 13.6 (56.five) | xix.ane (66.4) | 26.0 (78.8) | 31.8 (89.2) | 37.9 (100.2) | 40.3 (104.5) | 39.4 (102.9) | 34.9 (94.8) | 27.7 (81.9) | 18.9 (66.0) | 12.2 (54.0) | 26.0 (78.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.ii (39.half dozen) | vii.1 (44.8) | 12.0 (53.vi) | 18.3 (64.9) | 23.6 (74.five) | 29.1 (84.iv) | 31.8 (89.2) | 30.three (86.5) | 25.2 (77.4) | xix.0 (66.two) | xi.5 (52.7) | 6.ane (43.0) | eighteen.ii (64.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.9 (28.vi) | 0.6 (33.1) | v.0 (41.0) | 10.v (fifty.nine) | 15.4 (59.7) | 20.2 (68.4) | 23.4 (74.1) | 21.2 (70.2) | 15.6 (lx.1) | 10.3 (l.v) | iv.one (39.4) | −0.1 (31.eight) | 10.4 (l.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −23 (−9) | −11.2 (xi.8) | −xi (12) | 0.4 (32.7) | 5.4 (41.7) | 8.0 (46.4) | xv.0 (59.0) | 13.v (56.3) | half dozen.v (43.7) | 0.6 (33.1) | −7 (nineteen) | −10.5 (13.i) | −23 (−9) |
| Average atmospheric precipitation mm (inches) | 25.4 (ane.00) | xx.five (0.81) | 27.vii (i.09) | 20.ii (0.lxxx) | x.4 (0.41) | 2.3 (0.09) | 0.7 (0.03) | 0.3 (0.01) | 0.8 (0.03) | half-dozen.ii (0.24) | fourteen.three (0.56) | 19.four (0.76) | 148.2 (5.83) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 4.four | 4.one | four.2 | 3.9 | 2.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 2.vi | 3.2 | 27.2 |
| Average snowy days | three.one | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.one | 0.9 | 5.eight |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 66 | 58 | 48 | 42 | 33 | 24 | 23 | 24 | 26 | 38 | 52 | 66 | 41 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 185.0 | 194.0 | 221.five | 233.3 | 296.six | 351.five | 354.5 | 347.3 | 309.9 | 263.4 | 204.9 | 172.7 | 3,134.vi |
| Source: Iran Meteorological Arrangement (records),[39] (temperatures),[40] (precipitation),[41] (humidity),[42] (days with atmospheric precipitation and snow),[xi] (sunshine)[thirteen] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Ahvaz (1951–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record loftier °C (°F) | 28.0 (82.4) | 31.five (88.7) | 37.6 (99.7) | 43.0 (109.4) | 48.6 (119.5) | 51.0 (123.8) | 54.0 (129.2) | 51.6 (124.9) | 48.4 (119.one) | 45.0 (113.0) | 36.0 (96.8) | 29.0 (84.ii) | 54.0 (129.2) |
| Boilerplate high °C (°F) | 17.v (63.5) | xx.5 (68.9) | 25.5 (77.9) | 32.2 (ninety.0) | 39.3 (102.7) | 44.6 (112.3) | 46.iii (115.iii) | 45.nine (114.6) | 42.5 (108.v) | 36.0 (96.viii) | 26.v (79.seven) | 19.4 (66.9) | 33.0 (91.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 12.3 (54.1) | fourteen.7 (58.5) | xix.0 (66.2) | 24.9 (76.8) | 31.one (88.0) | 35.two (95.4) | 37.3 (99.1) | 36.7 (98.one) | 33.0 (91.4) | 27.3 (81.1) | 19.8 (67.6) | fourteen.0 (57.two) | 25.4 (77.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 7.2 (45.0) | 8.viii (47.eight) | 12.5 (54.five) | 17.6 (63.7) | 23.0 (73.four) | 25.9 (78.6) | 28.2 (82.viii) | 27.4 (81.iii) | 23.iv (74.1) | 18.viii (65.viii) | xiii.0 (55.iv) | 8.half-dozen (47.5) | 17.ix (64.ii) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −7.0 (19.iv) | −5.0 (23.0) | −one.0 (30.two) | 6.0 (42.eight) | 13.0 (55.4) | 15.0 (59.0) | 19.0 (66.2) | xviii.0 (64.4) | 13.0 (55.4) | 8.0 (46.4) | 0.0 (32.0) | −one.0 (30.two) | −seven.0 (19.four) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 48.two (1.90) | 26.ix (1.06) | 26.4 (i.04) | sixteen.1 (0.63) | 4.4 (0.17) | 0.4 (0.02) | 0.1 (0.00) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.two (0.01) | 6.4 (0.25) | 31.iv (ane.24) | 48.7 (1.92) | 209.2 (viii.24) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ i.0 mm) | 4.9 | iii.six | 3.half-dozen | 2.eight | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.9 | 4.5 | 24.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 71 | 61 | 51 | 41 | 28 | 22 | 24 | 28 | 29 | 38 | 53 | 69 | 43 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 174.7 | 193.2 | 214.1 | 233.eight | 284.4 | 326.2 | 336.1 | 331.2 | 301.eight | 263.5 | 209.5 | 176.iv | 3,044.9 |
Source: Iran Meteorological Organization (records),[43] (temperatures),[44]
| |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Kermanshah, Islamic republic of iran (1961–1990, extremes 1951–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | January | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | November | Dec | Year |
| Record loftier °C (°F) | 20.2 (68.4) | 21.8 (71.2) | 28.4 (83.1) | 33.vii (92.vii) | 38.5 (101.3) | 43.0 (109.four) | 44.one (111.4) | 44.0 (111.two) | twoscore.iv (104.seven) | 34.4 (93.9) | 28.4 (83.ane) | 25.4 (77.7) | 44.1 (111.4) |
| Average loftier °C (°F) | half-dozen.5 (43.seven) | eight.9 (48.0) | 14.3 (57.7) | xix.seven (67.5) | 25.eight (78.4) | 33.3 (91.9) | 37.8 (100.0) | 37.0 (98.six) | 32.five (ninety.5) | 25.0 (77.0) | 16.7 (62.1) | 9.vii (49.5) | 22.3 (72.ane) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.vi (33.1) | ii.5 (36.5) | 7.vii (45.9) | 12.7 (54.9) | 17.six (63.vii) | 23.six (74.five) | 28.ii (82.viii) | 27.2 (81.0) | 22.iv (72.3) | 16.0 (60.8) | 8.9 (48.0) | 3.five (38.3) | 14.2 (57.six) |
| Boilerplate low °C (°F) | −iv.3 (24.3) | −3.0 (26.six) | 1.2 (34.2) | 5.1 (41.2) | 8.2 (46.8) | eleven.four (52.5) | xvi.i (61.0) | xv.4 (59.7) | 10.6 (51.one) | 6.4 (43.5) | 1.eight (35.ii) | −1.seven (28.9) | v.half dozen (42.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −24 (−11) | −27.0 (−16.6) | −11.iii (xi.7) | −6.1 (21.0) | −i.0 (30.2) | 2.0 (35.half dozen) | viii.0 (46.4) | eight.0 (46.iv) | i.2 (34.ii) | −3.5 (25.vii) | −17.0 (1.4) | −17 (1) | −27.0 (−16.six) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 67.1 (2.64) | 62.9 (ii.48) | 88.9 (3.fifty) | 69.9 (2.75) | 33.vii (1.33) | 0.5 (0.02) | 0.3 (0.01) | 0.3 (0.01) | ane.3 (0.05) | 29.ii (1.15) | 54.3 (2.14) | 70.3 (ii.77) | 478.7 (18.85) |
| Boilerplate rainy days | eleven.four | 10.7 | 12.6 | 11.0 | 7.6 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | four.ix | vii.9 | 9.6 | 77.iii |
| Boilerplate snowy days | 5.ix | 4.seven | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.three | 3.1 | 16.i |
| Boilerplate relative humidity (%) | 75 | 71 | 62 | 57 | 49 | 28 | 23 | 23 | 25 | xl | 59 | 71 | 49 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 134.8 | 150.i | 180.7 | 204.half-dozen | 268.0 | 348.3 | 349.1 | 336.7 | 304.six | 242.eight | 187.vi | 147.9 | 2,855.2 |
| Source ane: NOAA [49] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Iran Meteorological Organization (records)[fifty] [51] | |||||||||||||
| Climate information for Rasht | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | October | November | Dec | Year |
| Tape high °C (°F) | xxx (86) | 31 (88) | 34.six (94.3) | 37 (99) | 37.6 (99.7) | 37 (99) | 37 (99) | 37.two (99.0) | 40 (104) | 37.four (99.3) | 36 (97) | 32 (xc) | 40 (104) |
| Boilerplate high °C (°F) | x.8 (51.four) | 10.ix (51.6) | 13.i (55.6) | nineteen.0 (66.2) | 24.2 (75.6) | 28.3 (82.ix) | thirty.5 (86.9) | 29.nine (85.8) | 26.8 (80.ii) | 21.7 (71.ane) | 17.7 (63.ix) | 13.6 (56.5) | 20.5 (69.0) |
| Average depression °C (°F) | one.9 (35.iv) | two.5 (36.5) | 5.1 (41.2) | 9.3 (48.7) | 14.2 (57.half-dozen) | 18.0 (64.4) | 20.2 (68.4) | 19.8 (67.6) | 17.ii (63.0) | 12.viii (55.0) | 8.3 (46.9) | 4.2 (39.half-dozen) | eleven.1 (52.0) |
| Tape low °C (°F) | −19 (−ii) | −eighteen (0) | −6.four (20.five) | −2 (28) | 3.half dozen (38.5) | v (41) | 11 (52) | 9 (48) | 7 (45) | 1 (34) | −4 (25) | −10 (14) | −xix (−two) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 147.ix (5.82) | 119.ii (4.69) | 111.iii (4.38) | 61.6 (2.43) | 53.three (2.10) | 38.7 (one.52) | twoscore.2 (1.58) | 73.8 (2.91) | 142.vi (v.61) | 230.2 (nine.06) | 170.seven (vi.72) | 166.0 (6.54) | 1,355.5 (53.36) |
| Average rainy days | eleven.7 | 10.7 | 12.0 | 8.6 | 7.seven | four.3 | 3.7 | 6.viii | 9.5 | 12.3 | 10.7 | 11.four | 109.iv |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 84 | 85 | 84 | 80 | 78 | 74 | 74 | 77 | 82 | 86 | 85 | 85 | 81.two |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 89.9 | 79.ane | 71.three | 114.0 | 161.2 | 204.0 | 210.viii | 167.4 | 138.0 | 108.5 | 93.0 | 86.8 | one,524 |
| Source 1: World Climate[52] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Shahrekord Meteorology Database[53] | |||||||||||||
| Climate information for Saqqez, Iran | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calendar month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | October | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.ii (64.8) | 20 (68) | 24 (75) | 29 (84) | 34.iv (93.ix) | 39 (102) | 43 (109) | 42 (108) | 39 (102) | 32 (90) | 26 (79) | 22.two (72.0) | 43 (109) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.4 (36.iii) | iv.7 (40.5) | 11.0 (51.viii) | 17.3 (63.i) | 23.1 (73.6) | 29.viii (85.6) | 34.3 (93.seven) | 34.2 (93.6) | 29.8 (85.6) | 22.two (72.0) | xiii.iv (56.1) | 6.1 (43.0) | 19.03 (66.25) |
| Boilerplate depression °C (°F) | −8.i (17.4) | −6.seven (19.ix) | −1.2 (29.8) | 3.6 (38.5) | 6.6 (43.9) | 9.5 (49.ane) | xiv.0 (57.two) | xiii.four (56.1) | eight.3 (46.9) | iv.4 (39.9) | −0.three (31.5) | −four.half dozen (23.7) | 3.24 (37.83) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −32 (−26) | −36 (−33) | −27.6 (−17.7) | −9 (16) | −5 (23) | −0.6 (xxx.nine) | iii.eight (38.8) | 4.8 (40.6) | −0.4 (31.3) | −7 (xix) | −24 (−11) | −32 (−26) | −36 (−33) |
| Average atmospheric precipitation mm (inches) | 66.6 (two.62) | 58.seven (2.31) | 79.5 (3.thirteen) | 83.6 (3.29) | 52.0 (two.05) | 5.8 (0.23) | ii.9 (0.11) | 2.5 (0.ten) | 1.four (0.06) | 27.eight (1.09) | 56.ix (2.24) | 61.vii (2.43) | 499.4 (nineteen.66) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ one.0 mm) | 8.5 | viii.iii | ten.0 | 9.8 | 7.0 | i.2 | 0.7 | 0.vi | 0.v | four.iii | half dozen.2 | 8.1 | 65.two |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 73 | 70 | 64 | 58 | 52 | twoscore | 35 | 33 | 33 | 47 | 63 | 71 | 53 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 121.five | 142.2 | 177.4 | 213.i | 287.1 | 345.1 | 357.4 | 344.iii | 311.1 | 254.3 | 174.1 | 123.4 | 2,851 |
| Source: Synoptic Stations Statistics | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Hamedan | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | October | November | Dec | Year |
| Tape high °C (°F) | 17.0 (62.6) | 19.0 (66.2) | 25.0 (77.0) | 28.0 (82.4) | 33.0 (91.4) | 39.0 (102.2) | twoscore.6 (105.1) | 39.4 (102.9) | 36.iv (97.5) | thirty.0 (86.0) | 23.0 (73.iv) | 18.8 (65.viii) | xl.6 (105.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.0 (35.6) | 4.3 (39.seven) | 11.5 (52.7) | 18.1 (64.6) | 23.9 (75.0) | 30.9 (87.half-dozen) | 34.9 (94.8) | 34.2 (93.6) | 29.8 (85.6) | 21.9 (71.4) | thirteen.seven (56.7) | 5.9 (42.6) | 19.3 (66.7) |
| Daily hateful °C (°F) | −four.6 (23.seven) | −two.2 (28.0) | 4.5 (40.one) | 10.4 (fifty.7) | xv.5 (59.9) | 21.3 (70.3) | 25.three (77.five) | 24.3 (75.seven) | 19.0 (66.2) | 12.1 (53.8) | 5.three (41.5) | −0.nine (thirty.four) | 10.8 (51.v) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −10.5 (13.ane) | −8.two (17.ii) | −2.1 (28.2) | 2.7 (36.nine) | 6.4 (43.5) | 9.8 (49.six) | thirteen.nine (57.0) | 12.8 (55.0) | seven.0 (44.half dozen) | ii.5 (36.5) | −2.1 (28.2) | −6.6 (20.1) | 2.1 (35.8) |
| Tape depression °C (°F) | −34 (−29) | −33.0 (−27.four) | −21 (−vi) | −12.0 (ten.four) | −3.0 (26.half-dozen) | 2.0 (35.6) | 7.0 (44.6) | 4.0 (39.2) | −four.0 (24.viii) | −vii.0 (19.4) | −xiv.v (v.ix) | −29 (−20) | −34 (−29) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 46.3 (i.82) | 43.6 (i.72) | 49.4 (1.94) | 49.8 (one.96) | 37.8 (ane.49) | 3.7 (0.15) | 2.0 (0.08) | 1.8 (0.07) | 0.8 (0.03) | 20.7 (0.81) | 26.9 (i.06) | 40.9 (1.61) | 323.vii (12.74) |
| Boilerplate rainy days | xi.6 | xi.one | 12.4 | 12.ane | nine.five | two.0 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.0 | v.6 | 6.8 | ten.1 | 85.1 |
| Average snowy days | eight.8 | viii.2 | 4.two | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 6.ix | 29.viii |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 73 | 64 | 56 | 50 | 36 | 31 | 31 | 34 | 48 | 61 | 73 | 53 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 131.eight | 137.1 | 174.v | 199.6 | 258.five | 341.8 | 342.7 | 322.2 | 295.half-dozen | 234.iii | 183.1 | 135.3 | 2,756.five |
| Source: NOAA (1961-1990)[54] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Yazd | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | October | Nov | December | Yr |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.0 (80.6) | 28.0 (82.4) | 32.0 (89.6) | 37.0 (98.6) | 41.0 (105.8) | 44.0 (111.two) | 45.0 (113.0) | 45.half-dozen (114.1) | 42.0 (107.vi) | 36.0 (96.8) | xxx.0 (86.0) | 27.iv (81.iii) | 45.half dozen (114.ane) |
| Boilerplate high °C (°F) | 12.9 (55.2) | 15.nine (lx.six) | 20.6 (69.1) | 26.0 (78.viii) | 32.two (ninety.0) | 37.2 (99.0) | 39.6 (103.3) | 38.1 (100.six) | 34.0 (93.2) | 27.6 (81.vii) | xix.iii (66.7) | 14.0 (57.2) | 26.5 (79.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.3 (43.3) | ix.0 (48.2) | 13.8 (56.8) | 18.seven (65.vii) | 24.5 (76.one) | 29.iv (84.9) | 31.7 (89.ane) | 29.nine (85.viii) | 25.4 (77.7) | xix.iii (66.7) | 11.vii (53.ane) | 6.9 (44.4) | eighteen.9 (66.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.3 (31.5) | 2.two (36.0) | seven.0 (44.vi) | eleven.5 (52.7) | 16.8 (62.2) | 21.vii (71.1) | 23.8 (74.viii) | 21.8 (71.2) | 16.nine (62.4) | eleven.0 (51.8) | 4.2 (39.half-dozen) | −0.ane (31.8) | 11.iv (52.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −14 (7) | −ten (14) | −7 (19) | 0.0 (32.0) | five.half dozen (42.ane) | 11.0 (51.eight) | 16.0 (sixty.viii) | 12.0 (53.vi) | 2.0 (35.6) | −3 (27) | −ten (xiv) | −sixteen (3) | −sixteen (three) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | seven.0 (0.28) | 0.eight (0.03) | 11.0 (0.43) | 21.nine (0.86) | 0.six (0.02) | 2.0 (0.08) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 3.0 (0.12) | 0.0 (0.0) | 2.0 (0.08) | 0.0 (0.0) | 48.3 (1.ix) |
| Boilerplate precipitation days | one | 3 | two | 11 | 1 | ane | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 23 |
| Boilerplate relative humidity (%) | 53 | 46 | 37 | 33 | 25 | eighteen | 17 | 18 | 19 | 27 | 38 | 47 | 32 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 181.6 | 203.0 | 207.5 | 230.nine | 293.nine | 334.i | 340.seven | 335.0 | 313.1 | 278.1 | 217.eight | 193.4 | 3,129.1 |
| Source ane: Climate-Data.org | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (extremes, sun, humidity, 1961–1990)[55] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Ardabil | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | January | February | Mar | April | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | November | Dec | Yr |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.2 (64.eight) | twenty.0 (68.0) | 27.2 (81.0) | 32.0 (89.6) | 33.0 (91.4) | 37.5 (99.five) | 38.0 (100.4) | 39.8 (103.six) | 37.4 (99.3) | xxx.viii (87.iv) | 25.0 (77.0) | 21.2 (70.2) | 39.eight (103.half dozen) |
| Average loftier °C (°F) | 3.0 (37.4) | iv.5 (40.1) | 9.3 (48.seven) | 16.seven (62.1) | 19.seven (67.5) | 23.2 (73.8) | 25.0 (77.0) | 24.seven (76.5) | 22.half dozen (72.seven) | 17.5 (63.5) | 11.four (52.5) | five.7 (42.3) | 15.three (59.five) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −7.nine (17.viii) | −half-dozen.3 (20.7) | −two.4 (27.seven) | ii.8 (37.0) | 6.0 (42.eight) | 9.0 (48.2) | 11.half dozen (52.9) | 11.six (52.9) | 8.7 (47.vii) | four.8 (40.6) | 0.iii (32.5) | −iv.half dozen (23.7) | 2.eight (37.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −31.4 (−24.5) | −33.8 (−28.8) | −28.eight (−19.8) | −13.0 (eight.half-dozen) | −8.five (xvi.seven) | −0.2 (31.six) | 3.0 (37.4) | 2.2 (36.0) | −4.four (24.i) | −21.0 (−v.8) | −24.2 (−11.6) | −27.0 (−xvi.half-dozen) | −33.eight (−28.8) |
| Average atmospheric precipitation mm (inches) | 25.3 (one.00) | 24.1 (0.95) | 40.ane (one.58) | 47.0 (1.85) | 42.6 (1.68) | 18.9 (0.74) | 5.9 (0.23) | v.5 (0.22) | ten.4 (0.41) | 31.8 (1.25) | 34.5 (ane.36) | 29.4 (i.16) | 315.5 (12.43) |
| Average rainy days | eight.2 | 8.9 | eleven.3 | 14.ii | xv.7 | 7.2 | three.ix | iv.1 | 6.4 | nine.two | seven.7 | 7.9 | 104.7 |
| Boilerplate snowy days | 7.6 | 7.vii | 7.i | ii.1 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.nine | 3.5 | 6.3 | 35.five |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 75 | 74 | 73 | 68 | 71 | 71 | 69 | 70 | 74 | 75 | 74 | 74 | 72 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 146.ii | 153.7 | 170.4 | 184.9 | 245.4 | 293.six | 302.8 | 274.3 | 227.1 | 185.6 | 153.iv | 141.0 | 2,478.4 |
| Source: [56] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Bandar Abbas (1961-1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | December | Twelvemonth |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.0 (89.vi) | 33.0 (91.iv) | 39.0 (102.ii) | 42.0 (107.6) | 47.0 (116.6) | 51.0 (123.viii) | 48.0 (118.4) | 46.0 (114.8) | 45.0 (113.0) | 42.0 (107.six) | 38.0 (100.iv) | 32.0 (89.6) | 51.0 (123.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 23.v (74.three) | 24.4 (75.9) | 27.7 (81.nine) | 31.six (88.9) | 36.3 (97.3) | 38.4 (101.1) | 38.2 (100.8) | 37.vii (99.9) | 36.8 (98.2) | 35.0 (95.0) | xxx.4 (86.7) | 25.v (77.9) | 32.13 (89.83) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | xviii.ane (64.6) | 19.4 (66.9) | 23.1 (73.half-dozen) | 26.8 (fourscore.2) | 31.2 (88.two) | 33.vii (92.7) | 34.4 (93.9) | 34.0 (93.two) | 32.5 (90.v) | 29.6 (85.three) | 24.iii (75.7) | 19.seven (67.5) | 27.2 (81.0) |
| Boilerplate low °C (°F) | 12.1 (53.8) | 14.0 (57.2) | 17.5 (63.five) | twenty.9 (69.6) | 24.seven (76.5) | 28.0 (82.4) | 30.iii (86.v) | 30.ane (86.2) | 27.7 (81.9) | 23.five (74.iii) | eighteen.0 (64.4) | xiii.5 (56.3) | 21.69 (71.04) |
| Record low °C (°F) | ii.3 (36.1) | 5.4 (41.7) | seven.6 (45.vii) | 11.5 (52.7) | 17.0 (62.6) | xx.0 (68.0) | 25.2 (77.4) | 25.0 (77.0) | 21.0 (69.8) | 12.0 (53.6) | 6.0 (42.eight) | 2.0 (35.6) | ii.0 (35.6) |
| Average atmospheric precipitation mm (inches) | 39.7 (ane.56) | 47.v (1.87) | 34.8 (1.37) | 10.7 (0.42) | 4.viii (0.19) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.6 (0.02) | 2.2 (0.09) | 0.8 (0.03) | 1.3 (0.05) | 5.0 (0.20) | 24.0 (0.94) | 171.4 (6.74) |
| Average atmospheric precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | iii.3 | 3.1 | 2.six | 1.3 | 0.two | 0.0 | 0.one | 0.2 | 0.one | 0.ane | 0.4 | 2.3 | 13.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 64 | 68 | 67 | 64 | 61 | 64 | 68 | 69 | 67 | 64 | 61 | 63 | 65 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 220.i | 211.9 | 232.five | 242.4 | 312.7 | 302.2 | 264.six | 270.1 | 270.1 | 283.4 | 251.ii | 228.eight | iii,090 |
| Source: NOAA (1961–1990)[57] [58] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Arak | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calendar month | Jan | February | Mar | April | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | December | Yr |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.0 (62.6) | 21.0 (69.eight) | 25.two (77.iv) | 29.0 (84.2) | 35.0 (95.0) | 41.0 (105.8) | 44.0 (111.2) | 41.0 (105.8) | 38.0 (100.4) | 31.0 (87.eight) | 24.0 (75.2) | xx.0 (68.0) | 44.0 (111.2) |
| Boilerplate high °C (°F) | 4.two (39.6) | six.8 (44.two) | 13.5 (56.3) | 19.6 (67.3) | 25.6 (78.one) | 32.6 (90.7) | 35.8 (96.iv) | 34.9 (94.8) | xxx.8 (87.4) | 23.one (73.half-dozen) | 14.8 (58.half dozen) | seven.6 (45.7) | twenty.8 (69.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −ane.3 (29.7) | i.0 (33.viii) | 7.3 (45.i) | thirteen.1 (55.half-dozen) | 18.4 (65.1) | 24.4 (75.ix) | 27.5 (81.5) | 26.3 (79.iii) | 21.9 (71.4) | 15.ii (59.4) | 8.0 (46.4) | 2.0 (35.6) | xiii.7 (56.six) |
| Boilerplate low °C (°F) | −5.7 (21.7) | −3.8 (25.2) | 2.0 (35.6) | seven.0 (44.6) | 11.0 (51.8) | 15.3 (59.v) | 18.8 (65.8) | 17.5 (63.5) | 13.0 (55.iv) | vii.eight (46.0) | 2.half dozen (36.seven) | −two.2 (28.0) | 6.ix (44.5) |
| Tape depression °C (°F) | −28 (−18) | −thirty.5 (−22.9) | −13 (ix) | −4.0 (24.eight) | 0.0 (32.0) | four.0 (39.ii) | 12.0 (53.6) | 10.0 (fifty.0) | 2.0 (35.six) | −four.0 (24.8) | −seven (19) | −23 (−9) | −30.5 (−22.9) |
| Boilerplate precipitation mm (inches) | 54.7 (2.fifteen) | 47.6 (1.87) | 53.one (2.09) | 53.4 (2.x) | 31.nine (1.26) | 1.v (0.06) | 0.half dozen (0.02) | 1.ane (0.04) | 0.7 (0.03) | eighteen.5 (0.73) | 31.6 (1.24) | 51.0 (2.01) | 345.vii (13.half dozen) |
| Average rainy days | 10.viii | 9.8 | xi.4 | 9.4 | seven.ane | one.i | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.vi | iv.iii | vi.1 | viii.9 | 71 |
| Average snowy days | 7.6 | half dozen.iv | 3.2 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | four.6 | 23.1 |
| Boilerplate relative humidity (%) | 72 | 67 | 55 | 46 | twoscore | 28 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 40 | 56 | 67 | 46 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 150.8 | 160.vi | 196.0 | 222.1 | 287.five | 350.four | 338.3 | 329.4 | 305.1 | 262.three | 188.5 | 160.8 | 2,951.eight |
| Source: NOAA (1961-1990) [59] | |||||||||||||
Flora and creature [edit]

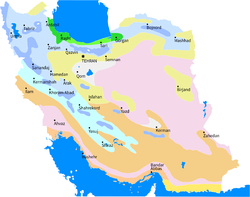
Map of biotopes of Iran
Forest steppe
Forests and woodlands
Semi-desert
Desert lowlands
Steppe
Salted alluvial marshes
7% of the state is forested. The most extensive growths are found on the mountain slopes ascent from the Caspian Bounding main, with stands of oak, ash, elm, cypress, and other valuable trees. On the plateau proper, areas of scrub oak appear on the all-time-watered mountain slopes, and villagers cultivate orchards and grow the plane tree, poplar, willow, walnut, beech, maple, and mulberry. Wild plants and shrubs jump from the barren land in the jump and afford pasturage, just the summertime sun burns them abroad. According to FAO reports,[sixty] the major types of forests that be in Islamic republic of iran and their respective areas are:
- Caspian forests of the northern districts – xix,000 km2 (seven,300 sq mi)
- Limestone mountainous forests in the northeastern districts (Juniperus forests) – 13,000 km2 (five,000 sq mi)
- Pistachio forests in the eastern, southern and southeastern districts – 26,000 kmtwo (10,000 sq mi)
- Oak forests in the central and western districts – 35,000 kmii (fourteen,000 sq mi)
- Shrubs of the Kavir (desert) districts in the central and northeastern part of the country – 10,000 km2 (3,900 sq mi)
- Sub-tropical forests of the southern coast, similar the Hara forests – five,000 km2 (one,900 sq mi)
Wild fauna of Iran is diverse and composed of several animal species including bears, gazelles, wild pigs, wolves, jackals, panthers, Eurasian lynx, and foxes. Domestic animals include, sheep, goats, cattle, horses, h2o buffalo, donkeys, and camels. The pheasant, partridge, stork, eagles and falcon are besides native to Iran.
As of 2001, 20 of Iran's mammal species and 14 bird species are endangered. Amidst them are the Baluchistan bear (Ursus thibetanus gedrosianus), a subspecies of Asian black bear, Persian fallow deer, Siberian crane, hawksbill turtle, green turtle, Oxus cobra, Latifi'southward viper, dugong and dolphins. The Asiatic chetah is a critically endangered species which is extinct elsewhere and now tin can merely be found in primal to northeastern parts of Iran.
Islamic republic of iran lost all its Asiatic lions and Caspian tigers past the earlier part of the 20th century. The Syrian wild donkey has become extinct. Syrian brown bears in the mountains, wild sheep and goats, gazelles, Persian onagers, wild pigs, Persian leopards, and foxes abound. Domestic animals include sheep, goats, cattle, horses, h2o buffalo, donkeys, and camels. The pheasant, partridge, stork, and falcon are native to Iran.
The Farsi leopard is said to be the largest of all the subspecies of leopards in the earth. The main range of this species in Iran closely overlaps with that of bezoar ibex. Hence, it is found throughout Alborz and Zagros mount ranges, as well as smaller ranges within the Iranian plateau. The leopard population is very sparse, due to loss of habitat, loss of natural prey, and population fragmentation.[ commendation needed ] Apart from bezoar ibex, wild sheep, boar, deer, (either Caspian cherry-red deer or roe deer), and domestic animals constitute leopards' nutrition in Islamic republic of iran.
Ecosystem and biosphere [edit]
Iran's bio-diversity ranks 13th in the world.[ citation needed ] At that place are 272 conservation areas around Iran for a full of 17 one thousand thousand hectares under the supervision of the Section of Surround (Iran), variously named national parks, protected areas, and natural wildlife refuges, all meant to protect the genetic resources of the land. In that location are only two,617 rangers and 430 environmental monitoring units engaged in protecting these vast areas, which amounts to half dozen,500 hectares to cover for each ranger.[61]
| Ramsar sites (23/06/75) | Area (km2) |
|---|---|
| Anzali Wetland Complex,[62] Gilan Province | 150 |
| Arjan Meadow,[63] Fars Province | 22 |
| Lake Gori,[64] Eastward Azerbaijan Province | 1.2 |
| Lake Kobi,[65] Westward Azerbaijan Province | 12 |
| Lake Parishan,[63] Fars Province | 40 |
| Miankaleh Peninsula, Gorgan Bay, Lapoo-Zaghmarz Ab-bandan[66] Mazandaran Province | 1000 |
Environmental concerns [edit]
Natural hazards: periodic droughts, floods; dust storms, sandstorms; earthquakes forth western border and in the northeast
Environment – current issues: air pollution, especially in urban areas, from vehicle emissions, refinery operations, and industrial effluents; deforestation; desertification; oil pollution in the Persian Gulf; wetland losses from drought; soil degradation (salination); inadequate supplies of drinkable water in some areas; h2o pollution from raw sewage and industrial waste; urbanization.
Resources and land use [edit]

Natural resource: petroleum, natural gas, coal, chromium, copper, atomic number 26 ore, lead, manganese, zinc, sulfur
arable land: 10.87%
permanent crops: 1.19%
other: 87.93% (2012 est.)
Irrigated country: 87,000 km2 (34,000 sq mi) (2009)
Full renewable water resources: 137 km3 (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agronomical):
full: 93.3 km3/yr (7%/1%/92%)
per capita: ane,306 thouthree/twelvemonth (2004)
Area and boundaries [edit]

Satellite view of southern Islamic republic of pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman
Surface area [68] :
full: one,648,195 km2 (636,372 sq mi)
land: 1,531,595 km2 (591,352 sq mi)
water: 116,600 kmii (45,000 sq mi)
Land boundaries:
total: v,894 kilometres (three,662 mi)
edge countries: Afghanistan 921 kilometres (572 mi), Armenia 44 kilometres (27 mi), Republic of azerbaijan-proper 432 kilometres (268 mi), Azerbaijan-Nakhchivan exclave 179 kilometres (111 mi), Iraq 1,599 kilometres (994 mi), Pakistan 959 kilometres (596 mi), Turkey 534 kilometres (332 mi), Turkmenistan 1,148 kilometres (713 mi).
Maritime boundaries: Qatar, Saudi arabia, United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman
Coastline: two,815 kilometres (i,749 mi)
note: Iran also borders the Caspian Sea, for 740 kilometres (460 mi)
Maritime claims:
territorial bounding main: 12 nmi (22.two km; 13.8 mi)
contiguous zone: 24 nmi (44.4 km; 27.6 mi)
sectional economic zone: 168,718 km2 (65,142 sq mi) with bilateral agreements, or median lines in the Persian Gulf
continental shelf: natural prolongation
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Caspian Sea −28 metres (−92 ft)
highest point: Mount Damavand 5,610 metres (18,410 ft)
International territorial disputes [edit]
Iran is currently engaged in international territorial disputes with several neighbouring countries.
The land protests Afghanistan's limiting flow of dammed tributaries to the Helmand River in periods of drought. The lack of a maritime boundary in the Persian Gulf with Iraq too prompts jurisdictional disputes beyond the rima oris of the Arvand Rud. Iran and the United Arab Emirates have a territorial dispute over the Greater and Bottom Tunbs and Abu Musa islands, which are administered by Iran. Iran currently insists on dividing the Caspian Body of water resource every bit among the 5 littoral states, afterward the Russian-backed old soviet breakaway republics refused to respect the l-50 agreements between Iran and the Soviet Union (despite their international obligation). Russia, Republic of azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan continue to claim territorial waters thus regarding the Caspian Sea every bit open international body of water, dismissing its geographically lake nature.[69]
- Photo gallery
-

Southern Alborz range near Firouzkuh
-

Maranjab dunes, Kavir desert, Kashan
-
-

-

-

Encounter likewise [edit]
- Armenian Highlands
- Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests
- Caspian Ocean
- Elburz Range forest steppe
- International rankings of Iran
- List of castles in Islamic republic of iran
- List of caves in Iran
- Listing of earthquakes in Iran
- Listing of Iranian four-thousanders
- Provinces of Islamic republic of iran
- Counties of Islamic republic of iran
- List of cities in Iran by province
- List of largest cities of Iran
- Counties of Islamic republic of iran
- Ramsar, Mazandaran: Highest natural radioactivity in the world
- Strait of Hormuz
Notes [edit]
- ^ Including the de facto independent, merely unrecognized Republic of Artsakh.
References [edit]
- ^ "Iran Country Profile". BBC News. Archived from the original on 25 November 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ^ ""CESWW" – Definition of Central Eurasia". Cesww.fas.harvard.edu. Archived from the original on v Baronial 2010. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ^ "Islamic republic of iran Guide". National Geographic. fourteen June 2013. Archived from the original on 12 December 2009. Retrieved 26 Nov 2014.
- ^ "Armenian Highland". Archived from the original on iii May 2015. Retrieved 28 Feb 2015.
- ^ "Glaciers of Iran – in pictures". The Guardian. 16 Dec 2014.
- ^ Murray, North.J.; Phinn, Southward.R.; DeWitt, M.; Ferrari, R.; Johnston, R.; Lyons, M.B.; Clinton, North.; Thau, D.; Fuller, R.A. (2019). "The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats". Nature. 565 (7738): 222–225. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0805-viii. PMID 30568300. S2CID 56481043.
- ^ *"Highest record temperature in Tehran past Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- "Lowest record temperature in Tehran by Calendar month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Arrangement. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ a b *"Boilerplate Maximum temperature in Tehran by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 6 September 2014.
- "Average Hateful Daily temperature in Tehran by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- "Average Minimum temperature in Tehran by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological System. Retrieved 20 March 2016. Cite error: The named reference "temperatures" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b "Monthly Total Precipitation in Tehran by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Cite error: The named reference "atmospheric precipitation" was defined multiple times with unlike content (see the assist page).
- ^ a b "Average relative humidity in Tehran by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Cite error: The named reference "humidity" was defined multiple times with different content (come across the help page).
- ^ a b "No. Of days with precipitation in Tehran by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Cite error: The named reference "precipdays" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "No. Of days with snowfall in Tehran by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization.
- ^ a b "Monthly total sunshine hours in Tehran past Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Cite error: The named reference "sunshine" was defined multiple times with unlike content (see the assistance page).
- ^ {{Cite web|url=https://www.conditions-atlas.com/en/iran/tehran-climate%7Ctitle=Tehran, Iran - Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast
- ^ I.R. OF Iran SHAHREKORD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION (IN PERSIAN) Archived 2017-08-29 at the Wayback Motorcar. 1988–2010
- ^ *"Highest tape temperature in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on iv February 2019. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- "Lowest record temperature in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 4 Feb 2019. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ *"Boilerplate Maximum temperature in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on viii March 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- "Average Mean Daily temperature in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 18 October 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- "Average Minimum temperature in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved eight April 2015.
- ^ "Monthly Total Precipitation in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on fifteen September 2018. Retrieved 8 Apr 2015.
- ^ "Average relative humidity in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ "No. Of days with atmospheric precipitation equal to or greater than ane mm in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 8 Apr 2015.
- ^ "No. Of days with snowfall in Mashhad by Calendar month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological System. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved viii Apr 2015.
- ^ "Monthly full sunshine hours in Mashhad by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Arrangement. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 8 Apr 2015.
- ^ "Esfahan Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 8 April 2015. [ expressionless link ]
- ^ "Highest tape temperature in Esfahan by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 25 Oct 2016. Retrieved 8 Apr 2015.
- ^ "Lowest record temperature in Esfahan past Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Arrangement. Archived from the original on four March 2016. Retrieved viii Apr 2015.
- ^
- "Highest record temperature in Karaj by Month 1985–2010". Iran Meteorological Organisation. Archived from the original on April 14, 2015. Retrieved Apr 7, 2015.
- "Lowest record temperature in Karaj by Month 1985–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on April fourteen, 2015. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- ^
- "No. Of days with precipitation equal to or greater than 1 mm in Karaj by Month 1985–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on April 14, 2015. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- "No. of days with snow or sleet in Karaj by Month 1985–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological System. Archived from the original on April 14, 2015. Retrieved April seven, 2015.
- ^
- "Monthly total sunshine hours in Karaj past Month 1985–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on April 14, 2015. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- ^ "Shiraz Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Assistants. Retrieved 7 Apr 2015.
- ^ "Highest record temperature in Shiraz by Calendar month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 14 April 2015. Retrieved vii April 2015.
- ^ "Lowest record temperature in Shiraz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 14 Apr 2015. Retrieved 7 Apr 2015.
- ^ *"Highest record temperature in Tabriz past Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 28 Feb 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- "Lowest record temperature in Tabriz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organisation. Archived from the original on 18 October 2018. Retrieved eight April 2015.
- ^ *"Average Maximum temperature in Tabriz by Calendar month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Arrangement. Archived from the original on 7 March 2016. Retrieved viii April 2015.
- "Average Mean Daily temperature in Tabriz by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 5 Feb 2020. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- "Average Minimum temperature in Tabriz past Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological System. Archived from the original on viii March 2016. Retrieved 8 Apr 2015.
- ^ "Monthly Total Precipitation in Tabriz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 11 September 2019. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ "Boilerplate relative humidity in Tabriz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on seven March 2016. Retrieved eight Apr 2015.
- ^ "No. Of days with precipitation equal to or greater than one mm in Tabriz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological System. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ "No. Of days with snow in Tabriz past Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on seven March 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ "Monthly total sunshine hours in Tabriz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^
- "Highest record temperature in Ghom by Month 1986–2010". Iran Meteorological Organisation. Retrieved viii April 2015.
- "Lowest record temperature in Ghom by Month 1986–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ *"Average Maximum temperature in Ghom past Month 1986–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on vi September 2014. Retrieved 8 Apr 2015.
- "Average Hateful Daily temperature in Ghom past Month 1986–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Retrieved viii April 2015.
- "Average Minimum temperature in Ghom by Month 1986–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 6 September 2014. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ "Monthly Total Precipitation in Ghom by Month 1986–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Retrieved eight April 2015.
- ^ "Boilerplate relative humidity in Ghom by Month 1986–2010". Iran Meteorological Organisation. Archived from the original on sixteen September 2014. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ *"Highest tape temperature in Ahwaz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- "Lowest record temperature in Ahwaz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 17 April 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ *"Boilerplate Maximum temperature in Ahwaz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 26 May 2016. Retrieved eight April 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)- "Average Mean Daily temperature in Ahwaz past Calendar month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 17 April 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- "Boilerplate Minimum temperature in Ahwaz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 30 May 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL condition unknown (link)
- ^ "Monthly Total Precipitation in Ahwaz by Calendar month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological System. Archived from the original on 9 Jan 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ "Boilerplate relative humidity in Ahwaz by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organisation. Archived from the original on 26 May 2016. Retrieved 8 Apr 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL condition unknown (link) - ^ "No. Of days with precipitation equal to or greater than 1 mm in Ahwaz past Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on iv March 2016. Retrieved eight April 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Monthly full sunshine hours in Ahwaz by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on five March 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL condition unknown (link) - ^ "Kermanshah Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Assistants. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ "Highest record temperature in Kermanshah by Month 1951–2010". Iran Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 5 Oct 2018. Retrieved 8 Apr 2015.
- ^ "Lowest record temperature in Kermanshah by Month 1951–2010". Islamic republic of iran Meteorological Organisation. Archived from the original on 21 November 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- ^ Rasht, Iran: Climate, Global Warming, and Daylight Charts and Information Archived 9 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on: June xvi, 2013.
- ^ Climatological Norms of Islamic republic of iran synoptic stations Archived xviii May 2013 at the Wayback Automobile. Retrieved on: September 12, 2011.
- ^ "Hamedan Nozheh Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 December 2012.
- ^ "Yazd Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 29 December 2012.
- ^ "آمار 166 ايستگاه سينوپتيك كشور تا پایان سال 2010 میلادی + 37 ایستگاه تا پایان سال 2005". Archived from the original on 17 Feb 2016. Retrieved thirteen Feb 2016.
- ^ "Bandar Abbas 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 29 December 2012.
- ^ "40875: Bandarabbass (Iran)". ogimet.com. OGIMET. 11 January 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ "Arak Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 Dec 2012.
- ^ "Unasylva – Vol. eight, No. 2 – The work of FAO". www.fao.org. Archived from the original on ix September 2007.
- ^ 74 Iranian wildlife species red-listed by Environment Section Archived 20 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine. (28 Feb 2014) Radio Zamaneh via Payvand Islamic republic of iran News. Retrieved 4 April 2014
- ^ "Ramsar Information Sheet: Anzali Wetlands Circuitous" Archived 27 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine, accessed 28 November 2008
- ^ a b "Ramsar Information Sail: Lake Lake Parishan and Dashte-Arjan" Archived 27 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine, accessed ane Dec 2008
- ^ "Ramsar Information Sheet: Lake Gori" Archived 27 March 2009 at the Wayback Auto, accessed 1 December 2008
- ^ "Ramsar Data Sheet: Lake Kobi" Archived 27 March 2009 at the Wayback Automobile, accessed i December 2008
- ^ "Ramsar Information Sheet: Miankaleh Peninsula, Gorgan Bay and Lapoo-Zaghmarz Ab-bandans" Archived 27 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine, accessed 28 Nov 2008
- ^ CSIS: The US, Israel, the Arab States and a Nuclear Islamic republic of iran Archived half-dozen August 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
- ^ "Land area (sq. km) – Data". data.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013.
- ^ CIA – The World Factbook – Iran
External links [edit]
- Geography of Persia, Encyclopædia Iranica:
- i. Evolution of geographical knowledge.
- 2. Man geography.
- three. Political geography.
- four. Cartography of Persia.
- Iran in Maps – BBC (population, land, infrastructure)
- Iran Geography
- Flora of Islamic republic of iran past Pr Ahmad GHAHREMAN
- Persia (Islamic republic of iran), Afghanistan and Baluchistan is a map from 1897
Coordinates: 32°00′Northward 53°00′E / 32.000°N 53.000°E / 32.000; 53.000
How Many Miles Is Iran,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geography_of_Iran
Posted by: cannonothympas.blogspot.com



0 Response to "How Many Miles Is Iran"
Post a Comment